Zadanie Optymalizacja dysku (opt)
Pomóż nam usprawnić bazę zadań!
Disk Optimization
Memory limit: 32 MB
A disk consists of 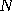 sectors numbered successively from
sectors numbered successively from 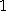 to
to 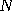 . Any nonempty sequence of sectors having consecutive numbers is
called a block. A length of a block is the number of sectors in the block.
Blocks are separate if they have no common sector.
. Any nonempty sequence of sectors having consecutive numbers is
called a block. A length of a block is the number of sectors in the block.
Blocks are separate if they have no common sector.
There are files written on a disk. A single file may be written on many sectors, which need not form a single block. To reconstruct a file correctly one needs to read those sectors in right order. This sequence of sectors determines a sequence of separate blocks - each of them contains one or more sectors. Sectors inside each block are read in order of their numbers.
A description of a file distribution on a disk is a sequence of pairs of positive integers. Each of these pairs comprises the number of the starting sector of a block and the length of the block.
Example
The sequence of pairs:
7 3 2 1 5 2informs that the contents of the file ought to be read successively from the sectors numbered: 7, 8, 9, next: 2, and next: 5, 6.
Each sector on a disk may be either free or there may be written a part of only one file (or one whole file).
Each file has a unique ID - a positive integer in the range of 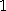 to
to
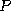 , where
, where 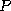 is the number of files on the disk.
is the number of files on the disk.
A disk is optimized when:
- each file is stored in one block (in consecutive sectors),
- a file with a smaller ID occupies sectors of lower numbers than every file with a greater ID,
- every free sector has a greater number than every occupied sector.
One may perform the following operations on a disk:
- copying the contents of a block to a separate block of the same length,
- swapping the contents of two separate blocks of the same length.
Copying a block of length 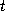 lasts
lasts 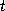 microseconds. Swapping
contents of two blocks of length
microseconds. Swapping
contents of two blocks of length 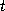 lasts
lasts 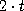 microseconds.
microseconds.
The instruction to copy a block has the form:
K start new_start lengthThe instruction to swap blocks has the form:
Z start1 start2 lengthK and Z are short forms of "kopiowanie" ("copying") and "zamiana" ("swapping"), and start is the number of the first sector of a block.
Task
Write a program that:
- reads from the standard input the number of sectors, the number of files and descriptions of their distributions on the disk,
- examines whether the disk is optimized. If so, the program writes only one word NIC ("nothing") to the standard output. If not, the program generates an appropriate sequence of instructions that optimizes the disk in the shortest time possible (the number of instructions is not important; only the collective time to perform all the instructions signifies); next the program writes the sequence of instructions to the standard output.
Input
In the first line of the standard input there are written two positive
integers: the number of sectors on the disk 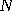 , not greater than
, not greater than
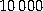 , and the number of files
, and the number of files 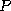 .
.
Next in the successive lines there are descriptions of file distributions on the disk.
Each file description contains two numbers in the first line: the file's ID
from the range of 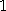 to
to 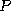 and a positive number denoting
the number of separate blocks the file is written in. In the next lines there is
the description of the file distribution in a form of an appropriate sequence of
pairs of positive integers, one pair per line.
and a positive number denoting
the number of separate blocks the file is written in. In the next lines there is
the description of the file distribution in a form of an appropriate sequence of
pairs of positive integers, one pair per line.
The numbers in lines are separated by single spaces.
The data in the standard input are written correctly and your program need not verify that.
Output
The standard output is to contain:
- either only one word NIC, when the disk is already optimized,
- or a sequence of instructions - one per line. Each instruction has to be written conforming to the format given above: first a capital letter K or Z, a single space, then three positive integers separated by single spaces.
Example
For the input data:
200 2 2 2 51 10 41 10 1 2 71 20 11 20
the correct result is:
K 21 31 10 K 11 21 10 K 71 1 20 Z 41 51 10
Task authors: Tomasz Smigielski, Piotr Krysiuk.
Kontakt
In the event of technical difficulties with Szkopuł, please contact us via email at [email protected].
If you would like to talk about tasks, solutions or technical problems, please visit our Discord servers. They are moderated by the community, but members of the support team are also active there.

 English
English