Zadanie Przyspieszenie algorytmu (prz)
Pomóż nam usprawnić bazę zadań!
Algorithm Speedup
Memory limit: 64 MB
As a punishment for misbehaving, Byteasar is to calculate a certain mysterious and nasty
Boolean-valued function 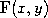 , which is defined for a pair of positive integer sequences
, which is defined for a pair of positive integer sequences
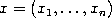 ,
,  as follows:
as follows:
boolean 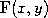
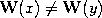 then return
then return 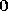
else if
 then return
then return 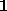
else return
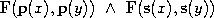 .
.
Where:
-
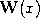 denotes the set of members of the sequence
denotes the set of members of the sequence  (order and repetitions of elements are insignificant),
(order and repetitions of elements are insignificant),
-
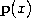 denotes the longest prefix (initial part of any length) of the sequence
denotes the longest prefix (initial part of any length) of the sequence  ,
such that
,
such that 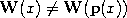 ,
,
-
 denotes the longest suffix (final part of any length) of the sequence
denotes the longest suffix (final part of any length) of the sequence  ,
such that
,
such that 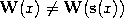 ,
,
-
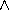 denotes the logical conjunction,
denotes the logical conjunction, 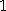 - true,
- true, 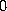 - false,
and
- false,
and 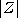 - cardinality of set
- cardinality of set 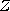 .
.
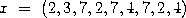 we have:
we have:
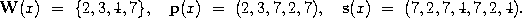 For very large data a programme calculating values of the function
For very large data a programme calculating values of the function 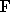 directly from definition is too
slow by any standards.
Therefore you are to make these calculations as fast as possible.
directly from definition is too
slow by any standards.
Therefore you are to make these calculations as fast as possible.
Write a programme that
reads several pairs of sequences  from the standard input and
prints out the values
from the standard input and
prints out the values 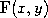 on the standard output for every input pair.
on the standard output for every input pair.
Input
The first line of the standard input contains one integer 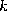 (
(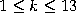 )
denoting the number of sequence pairs to analyse.
Next
)
denoting the number of sequence pairs to analyse.
Next 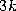 line hold descriptions of test cases.
The first line of each description contains two integers
line hold descriptions of test cases.
The first line of each description contains two integers  and
and 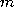 (
(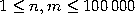 ) separated by a single space and denoting
the lengths of the first and second sequence, respectively.
The second line holds
) separated by a single space and denoting
the lengths of the first and second sequence, respectively.
The second line holds  integers
integers 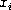 (
(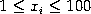 )
that form the sequence
)
that form the sequence  , separated by single spaces.
The third line holds
, separated by single spaces.
The third line holds 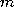 integers
integers 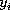 (
(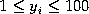 ),
that form the sequence
),
that form the sequence 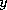 , separated by single spaces.
, separated by single spaces.
Output
The output should consist of exactly 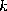 lines; the
lines; the 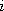 -th line (for
-th line (for 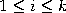 )
should contain a single integer - 0 or 1 -
the value of
)
should contain a single integer - 0 or 1 -
the value of 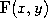 for
for 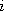 -th test case.
-th test case.
Example
For the input data:
2 4 5 3 1 2 1 1 3 1 2 1 7 7 1 1 2 1 2 1 3 1 1 2 1 3 1 3
the correct result is:
0 1
Task authors: Jakub Radoszewski and Wojciech Rytter.
Kontakt
In the event of technical difficulties with Szkopuł, please contact us via email at [email protected].
If you would like to talk about tasks, solutions or technical problems, please visit our Discord servers. They are moderated by the community, but members of the support team are also active there.

 English
English